Hikma launches ePHEDrine Sulfate Injection, USP in the US
London, 30 December 2024 – Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC (Hikma), the multinational pharmaceutical company, has launched ePHEDrine Sulfate Injection, USP in a 25 mg/5mL dosage in the US. The product is in a prefilled syringe and is indicated for the treatment of clinically important hypotension occurring in the setting of anesthesia.
According to IQVIA, US sales of ePHEDrine Sulfate Injection, USP, 25 mg/5mL, were approximately $17 million in the 12 months ending October 2024.
Hikma is a top three supplier of generic injectable medicines by volume in the US1, with a growing portfolio of more than 170 products. We are continuously expanding our portfolio of essential medicines and introducing new dosage forms that enhance patient care.
1Source: IQVIA MAT October 2024, generic injectable volumes by eaches, excluding branded generics and Becton Dickinson
This product has been approved for marketing in the United States by the US FDA. This product approval does not confer the right on Hikma, or any other party, to market this product outside the United States.
Important Safety Information for ePHEDrine Sulfate Injection, USP, 25 mg/5mL:
Please see package insert for referenced section/section numbering, where appropriate.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
WARNINGS & PRECAUTIONS
· Pressor Effect with Concomitant Oxytocic Drugs – Serious postpartum hypertension has been described in patients who received both a vasopressor (i.e., methoxamine, phenylephrine, ephedrine) and an oxytocic (i.e., methylergonovine, ergonovine). Some of these patients experienced a stroke.
· Tolerance and Tachyphylaxis – Data indicate that repeated administration of ephedrine can result in tachyphylaxis.
· Risk of Hypertension When Used Prophylactically – When used to prevent hypotension, ephedrine has been associated with an increased incidence of hypertension compared with when ephedrine is used to treat hypotension.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of ephedrine sulfate were identified in the literature. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting
Cardiac disorders: Tachycardia, palpitations (thumping heart), reactive hypertension, bradycardia, ventricular ectopics, R-R variability
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness
Psychiatric disorders: Restlessness
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Interactions that Augment the Pressor Effect
Oxytocin and oxytocic drugs: Serious postpartum hypertension has been described in patients who received both a vasopressor (i.e., methoxamine, phenylephrine, ephedrine) and an oxytocic (i.e., methylergonovine, ergonovine). Some of these patients experienced a stroke.
Clonidine, propofol, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), atropine: These drugs augment the pressor effect of ephedrine.
Interactions that Antagonize the Pressor Effect
These drugs antagonize the pressor effect of ephedrine. Examples include α-adrenergic antagonists, β adrenergic receptor antagonists, reserpine, quinidine, mephentermine.
Other Drug Interactions
Guanethidine: Ephedrine may inhibit the neuron blockage produced by guanethidine, resulting in loss of antihypertensive effectiveness.
Rocuronium: Ephedrine may reduce the onset time of neuromuscular blockade when used for intubation with rocuronium if administered simultaneously with anesthetic induction.
Epidural anesthesia: Ephedrine may decrease the efficacy of epidural blockade by hastening the regression of sensory analgesia.
Theophylline: Concomitant use of ephedrine may increase the frequency of nausea, nervousness, and insomnia.
Cardiac glycosides: Giving ephedrine with a cardiac glycoside, such as digitalis, may increase the possibility of arrhythmias.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from randomized studies, case series, and reports of ephedrine sulfate use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. However, there are clinical considerations due to underlying conditions.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryofetal risk
Untreated hypotension associated with spinal anesthesia for cesarean section is associated with an increase in maternal nausea and vomiting. A decrease in uterine blood flow due to maternal hypotension may result in fetal bradycardia and acidosis.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Cases of potential metabolic acidosis in newborns at delivery with maternal ephedrine exposure have been reported in the literature. These reports describe umbilical artery pH of ≤7.2 at the time of delivery. Monitoring of the newborn for signs and symptoms of metabolic acidosis may be required. Monitoring of infant’s acid-base status is warranted to ensure that an episode of acidosis is acute and reversible.
Lactation
Risk Summary
A single published case report indicates that ephedrine is present in human milk. However, no information is available on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ephedrine sulfate injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from ephedrine sulfate injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Ephedrine sulfate in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of ephedrine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Renal Impairment
Ephedrine and its metabolite are excreted in urine. In patients with renal impairment, excretion of ephedrine is likely to be affected with a corresponding increase in elimination half-life, which will lead to slow elimination of ephedrine and consequently prolonged pharmacological effect and potentially adverse reactions. Monitor patients with renal impairment carefully after the initial bolus dose for adverse events.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
General Dosage and Administration Instructions
Ephedrine sulfate injection, 25 mg/5 mL (5 mg/mL) in a prefilled syringe, is a premixed formulation. Do not dilute prior to use. The single-dose prefilled syringe is intended for use in one patient during one surgical procedure. Discard any unused portion. Inspect parenteral drug products visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Dosing for the Treatment of Clinically Important Hypotension in the Setting of Anesthesia
Ephedrine sulfate injection should be administered by trained healthcare providers. The recommended dosages for the treatment of clinically important hypotension in the setting of anesthesia is an initial dose of 5 mg to 10 mg administered by intravenous bolus. Administer additional boluses as needed, not to exceed a total dosage of 50 mg.
· Adjust dosage according to the blood pressure goal (i.e., titrate to effect).
Instructions for Use of Prefilled Syringe
1. Perform visual inspection on the syringe by verifying:
- Absence of syringe damage
- Absence of external particles
- Absence of internal particles
- Proper drug color
- Drug name
- Drug strength
- Fill volume
- Route of administration
- Expiration date to be sure the drug has not expired
2. Do not use if the plastic overwrap or the prefilled syringe has been damaged.
3. Remove the syringe from the plastic overwrap (see Figure 1). Do not pop syringe through.
Figure 1.
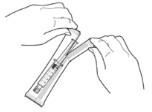
4. Push plunger rod slightly in to break the stopper loose while the tip cap is still on.
5. Remove tip cap by twisting off. (See Figure 2):
Figure 2.
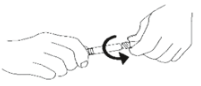
6. Discard the tip cap.
7. Expel air bubble.
8. Adjust dose into sterile material (if applicable).
9. Connect the syringe to an appropriate intravenous connection.
- Before injection, ensure that the syringe is securely attached to the needle or needleless luer access device (NLAD).
10. Depress plunger rod to deliver medication. Ensure that pressure is maintained on the plunger rod during the entire administration.
11. Remove syringe from NLAD (if applicable) and discard into appropriate receptacle.
- To prevent needle stick injuries, do not recap needle when needle is connected to syringe.
Note: All steps must be done sequentially
- Do not re-sterilize syringe
- Do not use this product on a sterile field
- Do not introduce any other fluid into the syringe at any time
- This product is for single dose only
OVERDOSAGE
Overdose of ephedrine can cause a rapid rise in blood pressure. In the case of an overdose, careful monitoring of blood pressure is recommended. If blood pressure continues to rise to an unacceptable level, parenteral antihypertensive agents can be administered at the discretion of the clinician.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ephedrine Sulfate Injection is indicated for the treatment of clinically important hypotension occurring in the setting of anesthesia.
HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP is a clear, colorless, sterile solution for intravenous injection supplied as follows:

Store Ephedrine Sulfate Injection, USP at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store in carton until time of use. For single-dose only. Discard unused portion. The single-dose 5 mL prefilled syringe is intended for use in one patient during one surgical procedure.
ENDING INFORMATION
For additional information, please refer to the Package Insert for full prescribing information, available on www.hikma.com.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. at 1-877-845-0689 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Manufactured by:
Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Berkeley Heights, NJ 07922 USA
